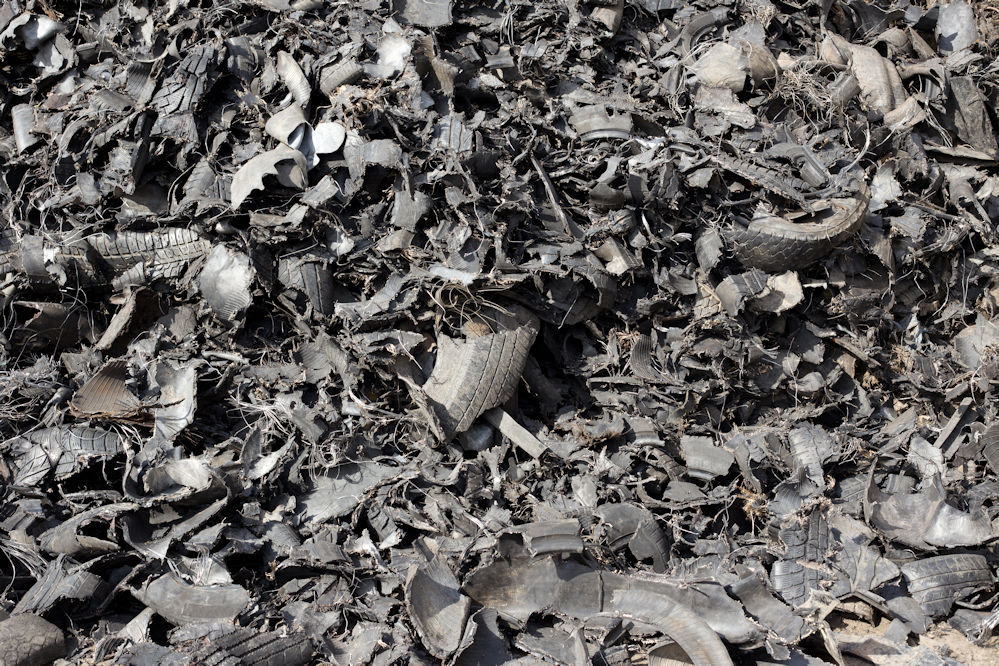
A TIA Statement on lends support to TDA (tyre derived aggregate) in roadways, bridges and water filtration
In the Statement, TIA outline the main uses they envisage for TDA.
All TDA applications described in the document use material that meets the ASTM D6270-B standard, ensuring consistent performance across road construction, structural backfill, and stormwater systems.
The document outlines TIA’s initiative to advance and promote the use of TDA in three primary application categories:
- Roads – Subgrade stabilization, frost protection, and drainage
- Walls and Bridge Structures – Lightweight backfill for bridge abutments and retaining walls
- Water Management Systems – Stormwater detention, infiltration, and runoff contaminant removal
The Statement outlines the positive gains from the use of TDA in mitigating poor subgrade conditions in roadways. TDA addresses issues around drainage and freeze-thaw cycles that can contribute to potholing and surface deterioration.
In walls and bridge abutments –Conventional soils used as backfill behind retaining walls and bridge abutments exert high lateral loads, particularly when saturated. Freeze-thaw cycles can further destabilize structures through moisture expansion and soil creep, often resulting in premature wall failure.
TDA, in compliance with ASTM D6270-B, is an ideal lightweight backfill material that reduces lateral static pressure—more than 50% less than traditional soil—and promotes rapid drainage. These characteristics help mitigate structural stress and prolong service life
In Water Management – the Stormwater Detention and Pollutant Capture Challenge: Urban runoff from rain events carries a high load of pollutants during the “first flush.” Traditional stormwater systems often lack the capacity to capture, retain, and filter this initial surge, resulting in flooding, erosion, and contamination of natural waterways
TDA, also compliant with ASTM D6270-B, serves as a cost-effective, high capacity medium for underground stormwater detention and infiltration systems. With the ability to store approximately 14 cubic feet of water per cubic yard, it also filters contaminants such as oil, heavy metals, and tyre wear particles from roadway runoff.
b not only aids in water quantity control but also supports water quality goals by serving as a filtration medium for pollutants commonly found in urban runoff.
TIA concludes that TDA is a proven, sustainable, and performance-enhancing material for infrastructure projects. All TDA described in the statement meets ASTM D6270-B standards, providing reliable and consistent performance in roadbeds, retaining structures, and stormwater systems.
TIA states that its commitment to advancing TDA usage is driven by its potential to solve real world engineering problems while providing an environmentally responsible outlet for recycled tyres. TDA’s use in roads, walls, and water systems presents a compelling case for its broader adoption in public and private sector projects. TIA will continue working with engineers, public agencies, and industry stakeholders to document performance, support education, and encourage widespread implementation of this valuable resource.