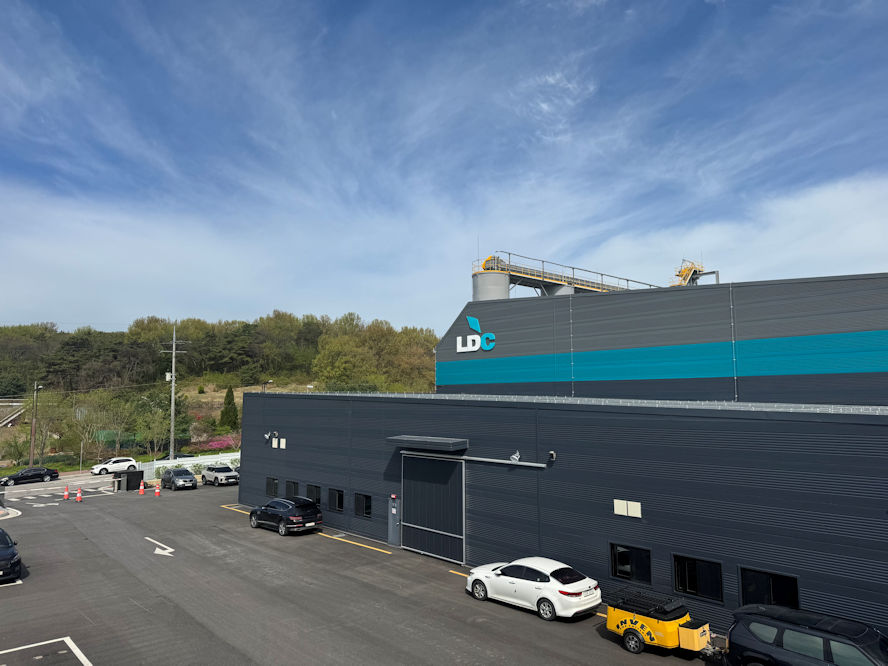
LD Carbon has opened Korea’s first and the largest tyre pyrolysis plant in Dangjin, South Korea
Every year approximately 400,000 tons of ELTs are generated in South Korea. Globally, the figure reaches 30 million tons annually. Most of these ELTs are recycled as construction materials or undergo heat treatment for pyrolysis oil extraction.
According to industry sources, even when pyrolysis oil is produced from ELTs, a volume of solid waste comparable to the produced oil is generated. South Korean companies involved in this business faced significant cost burdens due to processing nearly half of the input as waste.

Established in 2017, LD Carbon is a startup that has overcome the limitations of ELT recycling through technology. It transforms the byproduct, previously treated as waste, into rCB, which is used in the production of new tyres.
LD Carbon has established Korea’s first and the largest ELT resource circulation plant in Dangjin and held its completion ceremony on the 24th April.
The LD Carbon Dangjin plant is located in the ‘Dangjin Hapdeok General Industrial Complex.’ Upon entering the plant, built on a site of 29,800㎡ (approx. 9,000 pyeong), two factory buildings and five silos immediately catch the eye.
Tyre chips serve as the raw material for rCB, which, in turn, is used as a material for new tires. This creates a resource circulation structure: ‘End-of-Life Tyre → Tyre Chip → rCB → New Tyre.’
The tyre chips stored in the silos are moved to the ‘primary pyrolysis stage’. In this process, 10 pyrolysis units process up to 150 tons of tyre chips daily. Annually, this equates to a capacity capable of handling 50,000 tons of tyre chips.
Typically, after the primary pyrolysis stage, ELTs are transformed into pyrolysis oil and ‘char,’ a solid fuel.
LD Carbon further processes the char and performs secondary pyrolysis to produce rCB. Compared to conventional ‘Carbon Black’ used in tyre production, rCB can reduce carbon emissions by up to 32,000 tons.
rCB, extracted as a fine powder, can experience loss during delivery. Therefore, it undergoes another process to form small pellets before being supplied to customers. After completing this final process, LD Carbon’s ELT recycling rate reaches 98 per cent.
The Dangjin plant is projected to produce 20,000 tons of Green Carbon Black (LD Carbon’s rCB product name) and 24,000 tons of pyrolysis oil annually. This production volume surpasses the combined 7,000 tons previously produced at the pilot Gimcheon plant.
LD Carbon’s Dangjin plant has also achieved cost efficiency by automating almost all processes. An LD Carbon official explained, “99.9 per cent of the process is controlled by an automated system from the control room,” adding, “It’s structured for 24-hour continuous operation.”
rCB produced at LD Carbon’s Gimcheon plant is already being supplied to major domestic tyre companies. Furthermore, global tyre companies are also testing LDC’s rCB product.
Tire companies are reaching out to LD Carbon because its rCB holds the ‘ISCC PLUS‘ eco-friendly certification, which complies with European energy directives.
With major tyre companies aiming to achieve over 40 per cent sustainable raw material usage by 2030, the demand for rCB produced by LD Carbon is expected to increase further.
While rCB is the company’s core competitive strength, the pyrolysis oil generated from the primary pyrolysis stage also meets the eco-friendly demands of corporations.

Consequently, SK Incheon Petrochem has contracted to receive a 10-year supply of the pyrolysis oil that LD Carbon plans to produce in the future.
LD Carbon is set to begin full-scale operation of the Dangjin plant in April, is also pursuing the establishment of overseas factories, planning to enter the Asian market in the near future.
Yong Kyung Hwang, Co-CEO of LD Carbon, stated, “For rCB, we are receiving orders nearly double our production capacity. Our goal is to achieve a turnaround this year by operating the plant effectively.”