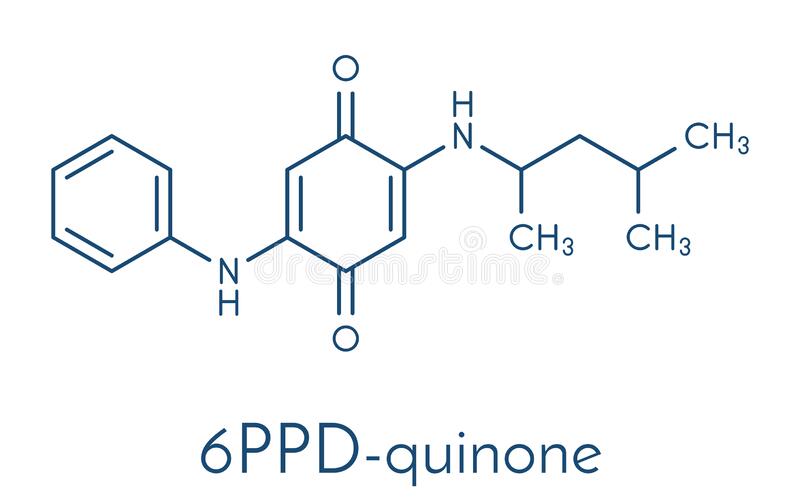
6PPDD-q is a derivative of 6PPD used as an additive in tyres; the derivative has been shown to be toxic in freshwater
The US Environment Protection Agency acted upon issues raised by indigenous tribes in Washington and Oregon, and other groups about the instances of Coho salmon young being killed off by the presence of 6PPDq in the rivers.
In November 2023, the EPA committed to gather evidence to be used to create regluations.
The U.S. EPA has now announced the publication of a draft testing method (EPA Method 1634) that will enable government agencies, Tribes, and other groups to determine where and when 6PPD-quinone is present in local stormwater and surface waters. The 6PPD-quinone draft method is now available at https://www.epa.gov/cwa-methods.
“We heard from the Tribes and other governmental agencies that one of the highest priorities for the agency should be the rapid development of a test for 6PPD-quinone,” said Casey Sixkiller, Regional Administrator of the agency’s Region 10 office in Seattle.
6PPD is also found in manyrubber products such as tyres, footwear, synthetic turf infill, and synthetic playground surfaces. 6PPD reacts with ozone in the air to form 6PPD-quinone, which EPA-funded research in 2020 found to be linked to the deaths of coho salmon in urban Puget Sound streams. Exposures occur when runoff containing the chemical is washed from parking lots and streets into streams and other bodies of water.
This new, quick testing method will allow authorities to better understand how and where 6PPDq is present in the watercourse. Although only in its draft format, the test is available to use already.